⚛️ Atom Structure
Learn about what makes up everything
What is an Atom?
Atoms are the building blocks of all matter in the universe. Everything you see is made of them. The computer you are using right now, the chair you are sitting on, the air you are breathing, even you are made of atoms. Atoms have a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in energy levels or shells.
Main Idea: Atoms are the building blocks of all matter in the universe.
Fun Fact: An atom is mostly empty space, and in between atoms is also mostly empty space. This means that everything that looks solid (eg. a cloud, a chair, the floor), is really just empty space.
Atomic Components
Protons
- • Positive charge (+1)
- • Located in the nucleus
- • Mass ≈ 1 atomic mass unit
- • Determines the element
Neutrons
- • No charge (neutral)
- • Located in the nucleus
- • Mass ≈ 1 atomic mass unit
- • Contributes to mass
Electrons
- • Negative charge (-1)
- • Orbit around nucleus
- • Very small mass
- • Determine bonding
Atom Structure
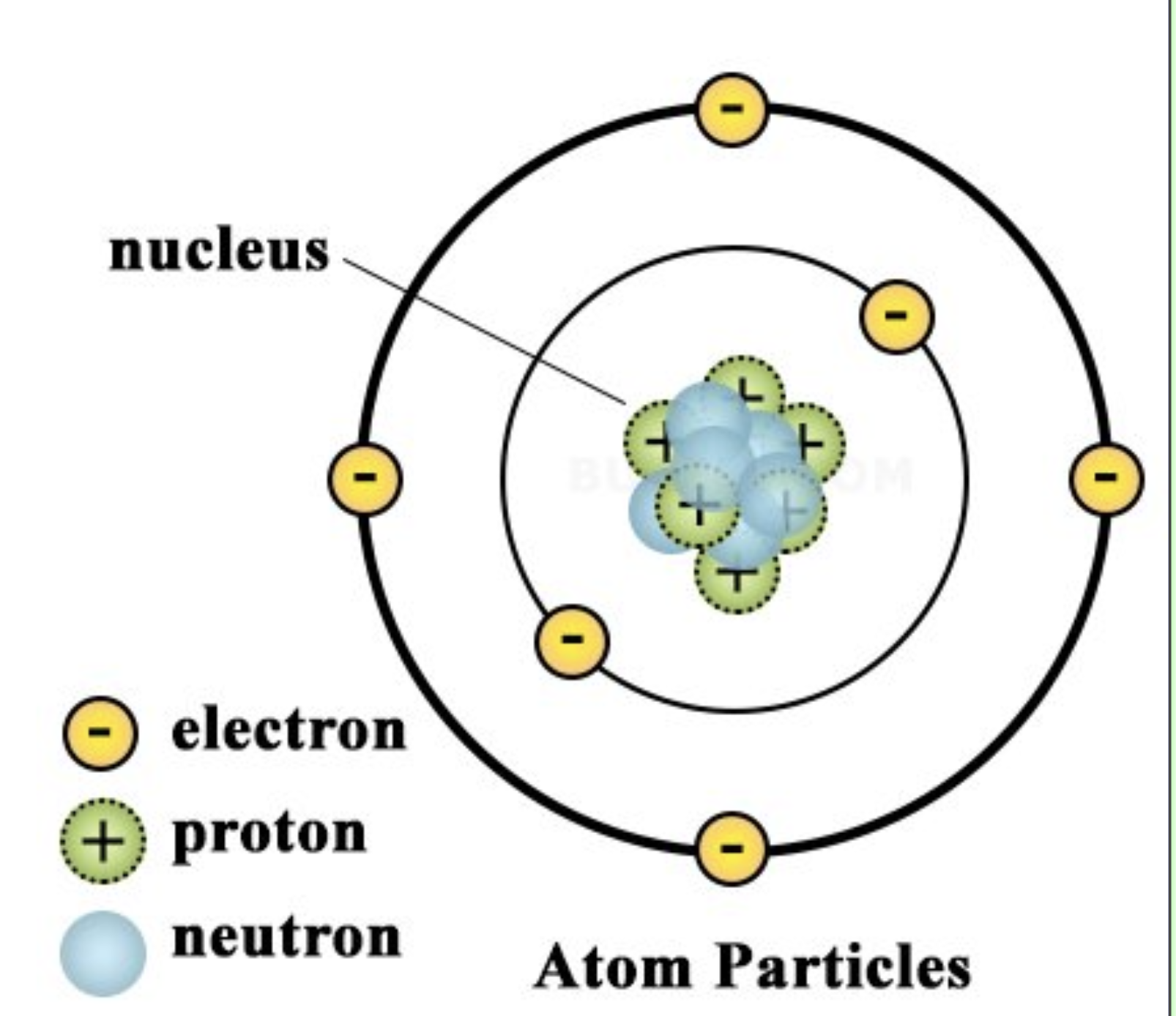
Atomic structure showing nucleus and electron shells. (In reality, atoms are 3d, but teachers like to simplify it.)
Energy Levels (Electron Shells)
Electrons are arranged in energy levels around the nucleus. Each level can hold a specific number of electrons:
Shell 1 (K-shell)
Maximum 2 electrons
Shell 2 (L-shell)
Maximum 8 electrons
Shell 3 (M-shell)
Maximum 18 electrons
Shell 4 (N-shell)
Maximum 32 electrons
Atomic Number and Mass
Atomic Number (Z)
The number of protons in the nucleus. Each element has its own unique number. For example, if on a quiz you are asked "What is the element with the atomic number of 6", there is only one correct answer - Carbon!
Example: Carbon has 6 protons, so Z = 6
Mass Number (A)
The sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
Example: Carbon-12 has 6 protons + 6 neutrons = 12
Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. They have the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
Carbon Isotopes Example:
Lazy Read
- • Atoms are the smallest units of matter that retain element properties
- • The nucleus contains protons (positive) and neutrons (neutral)
- • Electrons (negative) orbit the nucleus in energy levels
- • Atomic number = number of protons (determines the element)
- • Mass number = protons + neutrons
- • Isotopes have the same protons but different neutrons